how are qualified annuities taxed
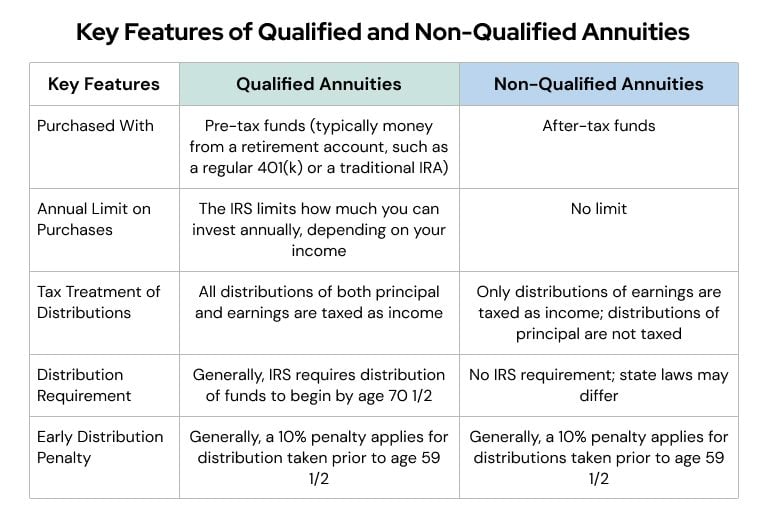
A qualified annuity is a savings plan for retirement. Non-qualified annuities are generally funded with after-tax contributions.

How Much Taxes Should I Plan On Paying For My Annuity Valuewalk
You put in money before taxes.
. The withdrawal of funds from a retirement annuity is taxed as ordinary income. Qualified annuities are funded with pre-tax dollars while non-qualified annuities are funded with post-tax dollars. In retirement just as when you were employed you get an income tax threshold known as your personal allowance.
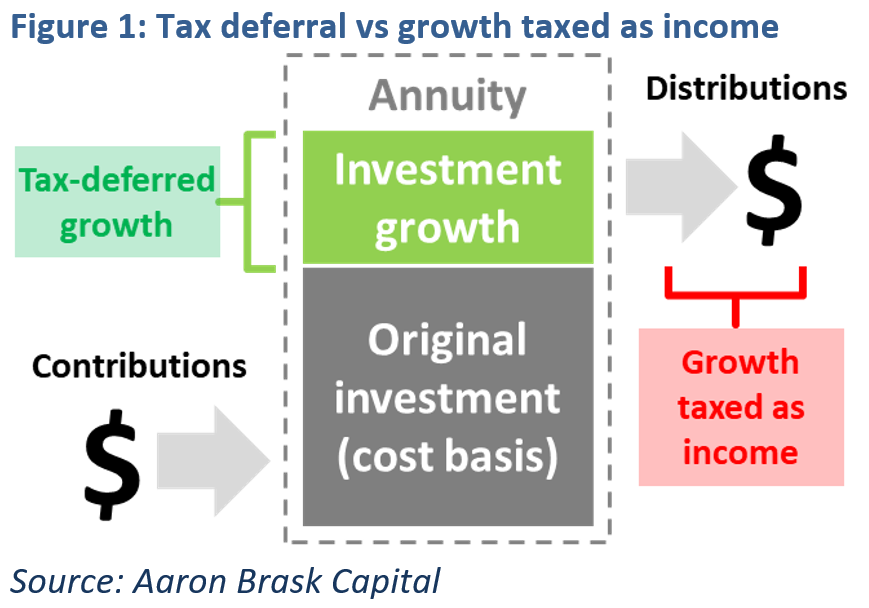
In addition to determining taxable annuity income. Until you receive your annuity distributions or stream of income taxes are deferred. Thats because you have not paid any taxes on them to date.
You fund a qualified annuity with pre-tax money money you have yet to pay taxes on. They can be purchased in retirement accounts or held as free-standing contracts. The benefits of non-qualified annuity taxation.
How A Qualified Annuity Works. A non-qualified annuity uses post-tax dollars. Based on whether you purchased the annuity with qualified pre.
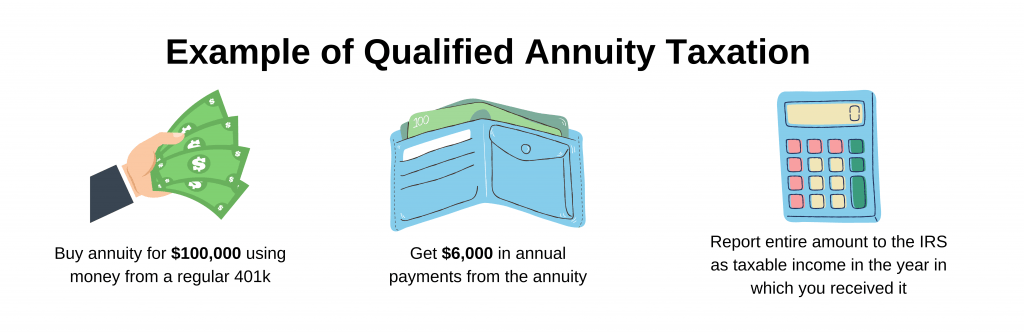
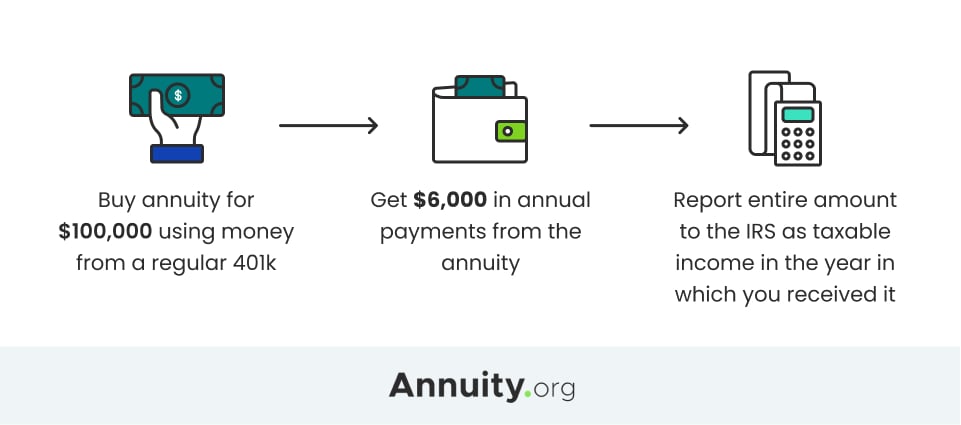
For 2021-22 the personal allowance is set at 12570 meaning. Buy an annuity for 10000 using money from a regular 401 k. Your annuity income payments are classed as earned income and are subject to income tax just like the salary you will have received during your working life.
Interest or earnings are taxed as ordinary income but the initial deposit or premium is not taxable. Marginal tax rates range from ten percent to thirty-seven percent for 2019. A non-qualified annuity is a saving plan for retirement that you put in post-tax dollars.
This means you only pay taxes on the earnings or interest amount of the distribution. It only becomes taxable once you begin receiving the funds from your annuity. Qualified annuities are funded with pre-tax dollars.
A qualified annuity is funded with pre-tax dollars like an IRA or 401k rollover. In the case of qualified annuities. Qualified immediate annuities.
A qualified annuity is a financial product that accepts and grows funds and is funded with pre-tax dollars. An annuity funded with pre-tax dollars is often a qualified annuity. Because the funds in a pretax qualified annuity have never been taxed the total amount of the payments received each year is.
Understanding which one you have will make a big difference come tax time. There are however two main taxation categories. How Qualified Annuities Are Taxed.
The difference between qualified and non-qualified tax status is significant because it affects how annuities are taxed for income. The beneficiarys relationship to the purchaser and the payout option thats selected can determine how an inherited annuity is taxed. The biggest benefit of an annuity is that your investment can grow on a tax-deferred basis.
Regardless of your age if you. Qualified annuities are those purchased through a qualified plan like a 401k or SIMPLE IRA and are normally paid for with pre-tax dollars. Once the money is in the account it continues to grow tax-deferred.
When you receive payments from a qualified annuity those payments are fully taxable as income. Non-qualified annuities are taxed based on what is called the exclusion ratio. Qualified annuities are purchased with pre-taxed income.
Owners of qualified annuities are required by law to begin taking distributions at the age of 72. Funds for a qualified annuity typically come directly from a 401k a Roth IRA or other tax-deferred individual retirement account. Withdrawals before age 595 may also be subject to additional state and federal income taxes and an additional early.
But annuities purchased with a Roth IRA or Roth 401 k are completely tax-free if certain requirements are met. Contributions to a qualified annuity are taken from your earnings and set aside in the retirement plan to. Qualified annuities must follow the Required Minimum Distribution RMD requirements.
What youll pay in taxes for an inherited annuity can depend on whether the annuity is qualified or non-qualified. This means you will pay taxes as normal income in the year you take a. Tax-Qualified A tax-qualified annuity is a retirement savings plan funded with.
How Qualified Annuities Are Taxed. There is a 10 federal income tax withholding on annuity withdrawals paid before age 595 unless you qualify for an exception due to your status as a government employee or church employee. Annuities can be tax-qualified or non-qualified.
The Internal Revenue Service IRS taxes the withdrawal of funds from a retirement annuity at the taxpayers marginal tax rate. The difference comes from the IRS. In this case the tax rules governing qualified plans and IRAs essentially trump the annuity tax rules which generally means that the full annuity payout is taxed as ordinary income.
For example if your annuity is part of an employer-sponsored retirement plan like a 401k or a SIMPLE IRA you may be able to make pre-tax contributions. If youre under 59 and 12 youll have to pay an early withdrawal penalty fee of 10 to the IRS on the full amount. Nonqualified variable annuities dont entitle you to a tax deduction for your contributions but your investment will grow tax.
This means you need to start taking distributions from the annuity by April 1 of the year after you turn 72.

How Are Annuities Taxed For Retirement The Annuity Expert
Annuity Taxation How Various Annuities Are Taxed

Qualified Vs Non Qualified Annuities Smartasset

Qualified Annuity What Is It And How Does It Work 2022

What S The Difference Between Qualified And Non Qualified Annuities

How Are Annuities Taxed For Retirement The Annuity Expert
How To Optimize Fixed Annuity Tax Deferral
Qualified Vs Non Qualified Annuities Taxes Rmd Retireguide
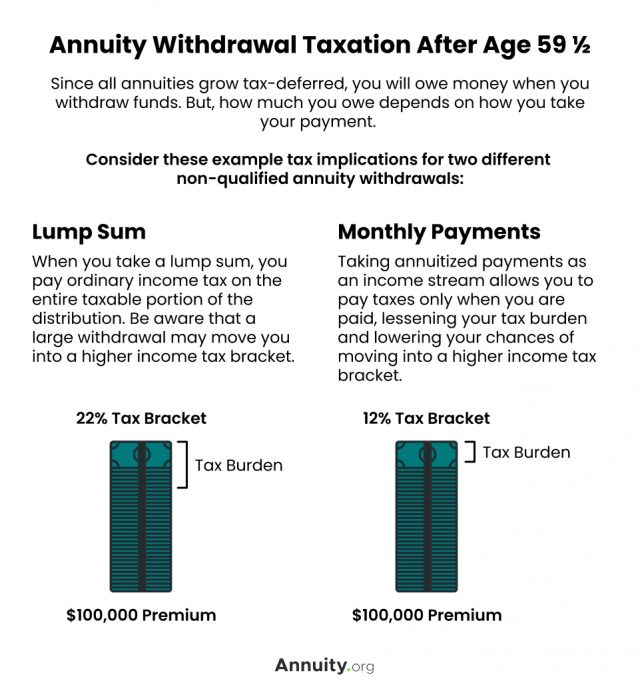
Annuity Taxation How Various Annuities Are Taxed

Start A Black Business On Instagram Startablackbusiness Teachothersaboutfinances Money Management Advice Personal Quotes Money Games

How Are Annuities Taxed For Retirement The Annuity Expert
How Is My Annuity Taxed Annuity 123 Annuity 123
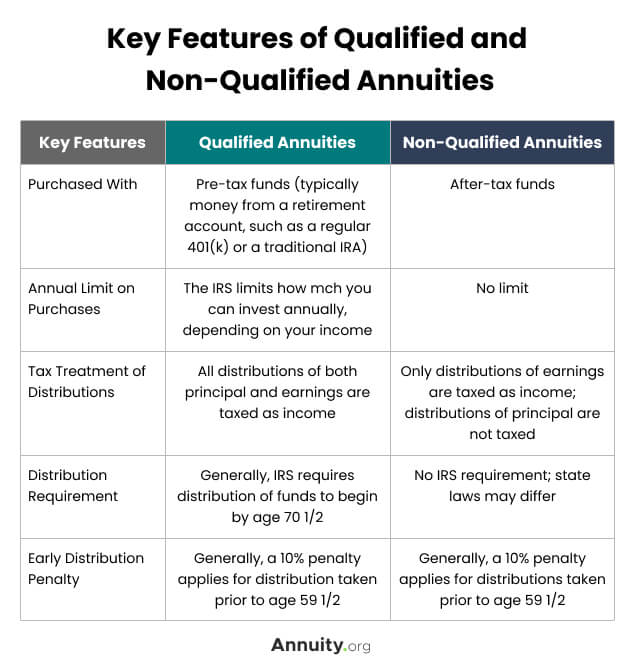
Qualified Vs Non Qualified Annuities Taxation And Distribution
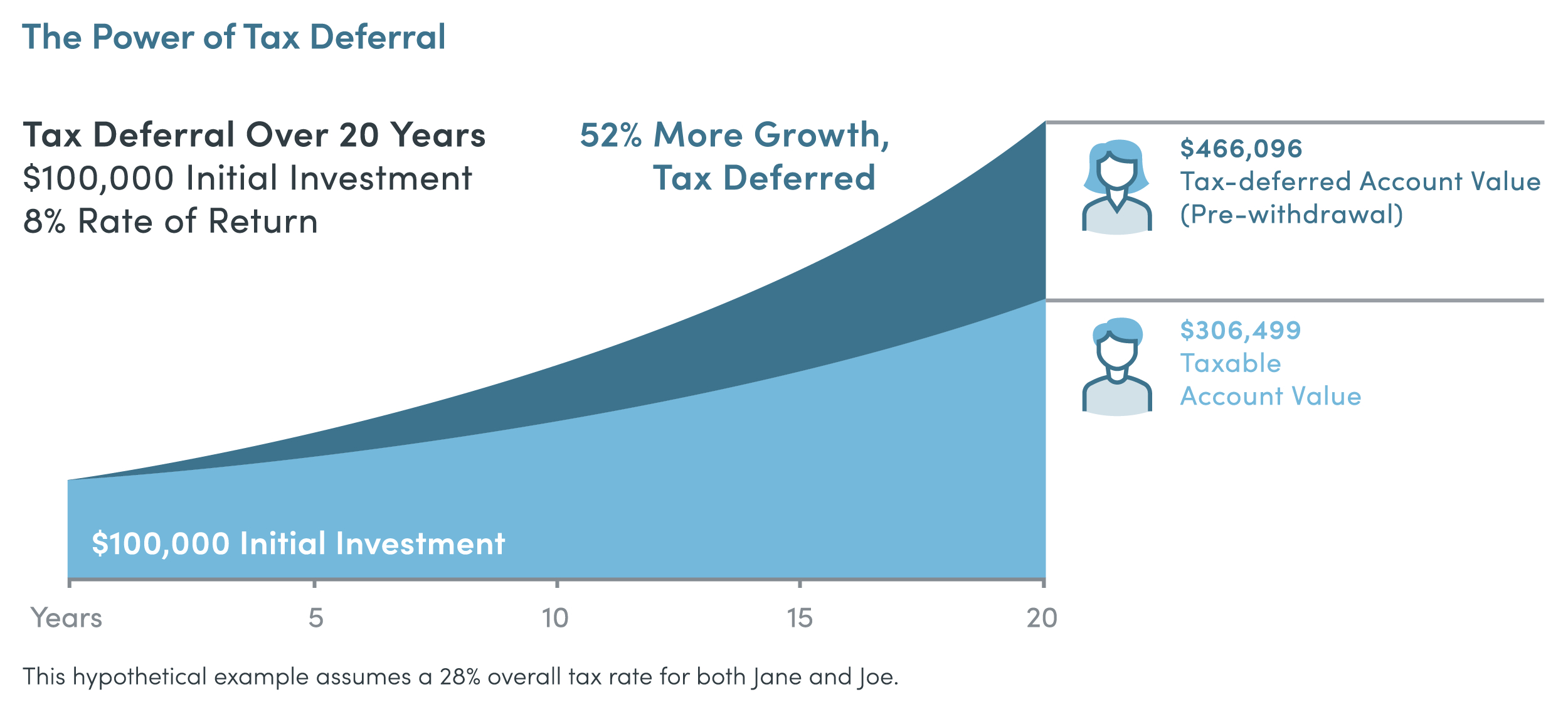
Make Saving For Your Future Less Taxing Security Benefit

How To Optimize Fixed Annuity Tax Deferral
Difference Between Qualified And Non Qualified Annuity Difference Between

Annuity Tax Consequences Taxes And Selling Annuity Settlements